Create basic geometric shapes and objects
Topics in this section
- Basic drafting skills
General information about creating objects - Selection
Selecting and deselecting objects - Construction Objects
Datum points and guides. - Lines
Drawing and editing line segments - Poly-lines
Create polygonal shapes with mixed line and arc segments - Polygons
Create closed rectangles and regular polygons - Hatches and fills
Closed regions filled with hatch, color or texture - Arcs, circles and ellipses
Drawing circles and circular arcs, ellipses and elliptical arcs - Curves
Drawing bézier paths and splines. - Images
Inserting images into the project - Groups
Group objects together into a single object - Symbols
Create reusable components
Basic Drafting Skills
The basic process of drawing any object in HighDesign consists of selecting the desired tool, choosing a drawing method from those available in the tool and clicking on the drawing area to start the construction of the object. If there are selected objects, the first click deselects everything.
New objects are created using the current default graphic attributes and properties: layer, stroke and fill, line-type, etc. If the object being created is an element, that is, an object that is more complex than a basic shape such as hatches or texts, you can set the specific defaults via its Settings window. Double-click the tool icon on the toolbox to open the Settings window for that class of objects.
Attributes and properties can also be changed at any time after the object has been created: select the object and change the desired properties.
Drawing Techniques
The default drawing procedure adopted in HighDesign is “Click-Move-Click,” i.e. to draw a line you click to set the start point, move the pointer to the desired location and click again to set its end point. Click-drag is also supported. You can change the drawing method in Preferences ▸ Drawing.
To cancel an operation you can hit the “Esc” button on the keyboard, or press the right mouse button.
Multi-segment objects, such as polylines, hatches, paths, follow the same general method: click to define the vertices, double-click or press the Esc key to end.
The general drafting procedures described above are also valid for Drafting, Documentation and Design tools.
Selection
The Arrow tool lets you select drawing objects by clicking directly on them or by defining a selection area. To select an object, click on it with the arrow tool. Snap to Objects must be active so that the arrow tool can “see” the object you are clicking.
Methods
Rectangular selection
Click on a blank part of the screen and move the pointer to define a rectangle: objects with control points within the rectangle will be selected.
If you move top-to-down, the selection will include all partially or fully enclosed objects (inclusive selection); if you move down-to-top, the selection will include only fully enclosed objects (exclusive selection). You can invert the selection mode at any time by holding down the Alt (Option) key.
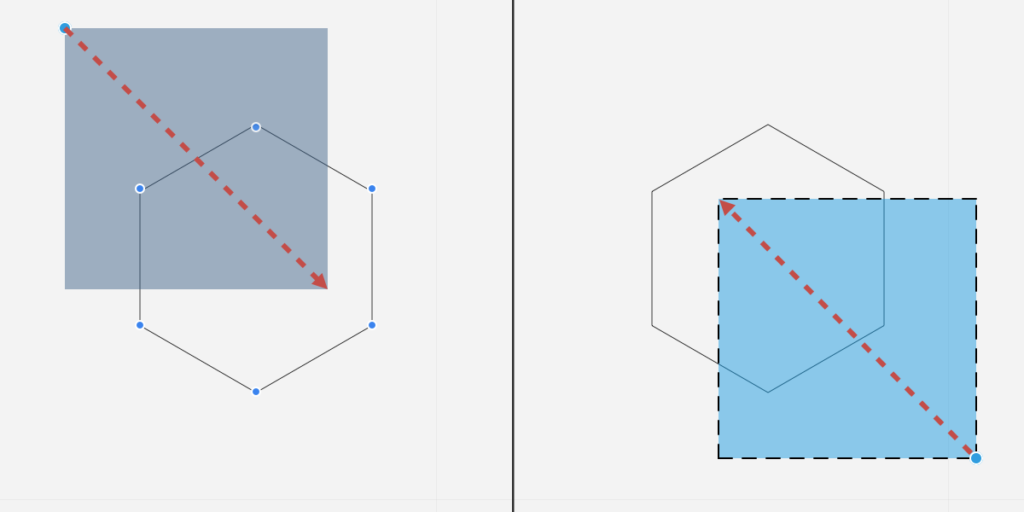
Polygonal selection
Use this method to select objects by defining a polygonal region. Click to add a vertex to the selection region, double-click to end
Adding and removing objects
Hold down the Shift key while clicking to add items to the selection or remove already selected items. Click on a blank part of the screen to deselect all. If the option “Arrow tool clicks extend selection” is active in Preferences, clicking an unselected object will automatically add it to the selection.
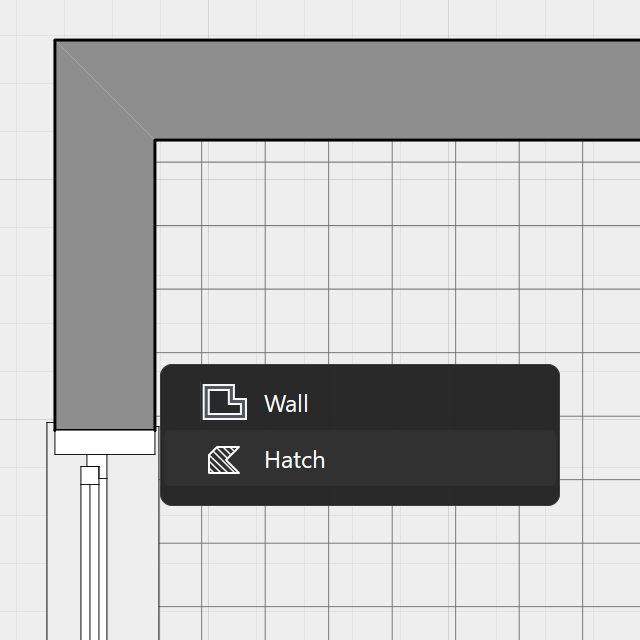
Selecting overlapping objects
When two or more items overlap it can be difficult to select the right object. To get a smart selection, activate the Arrow tool, hold the Control key and click or right-click on the intersection to open a contextual menu with a list of all the objects at that location, from top to bottom.
Editing objects
The Arrow tool can also be used as an all-purpose editing tool: most of the tool-specific editing actions, such as resizing a line or editing a text, can also be performed with the Arrow tool.
- Clicking a selected object on its outline, but not on a vertex, will activate the Move function.
- Clicking a vertex of an object resizes the object.
- Hovering the cursor on a vertex of a selected hatch, polyline or spline opens the menu with the options to edit the vertex.
- Hold down the Command key to move any object, selected or unselected, by any of its vertices or by its outline.
Construction Objects
The Construction Objects tool can be used to mark reference elements and auxiliary objects in the drawing. It has three modes: point, to create reference points in the drawing; construction line, to add infinite lines for alignments and margins; origin, to set the origin of the coordinate system in the current drawing.
Methods
Datum Point
Click on the desired location to insert a point or press the X and Y keys on the keyboard to enter its coordinates. In the Print window you can choose to print datum points and construction lines.
Construction Line
This method allows you to create guides, that is infinite lines that serve as references in the drawing. Construction lines can be created with two methods:
Guide from rulers
When the rulers are visible in the main drawing area (View ▸ Show Rulers), click and drag on the horizontal or vertical ruler to place an aligned guide. You can snap to drawing objects while dragging to place the guide at the desired location. This method works with any drawing tool.
Guide by point
With this method you can create a construction line oriented at an arbitrary angle.
- Activate the Construction Objects tool > Construction Lines method.
- Click to set the center and define the direction with the pointer. You can enter a definite angle by pressing the A key on the keyboard or clicking an existing linear object to draw a parallel construction line. To set the distance of the construction line from the reference linear object, press the L key on the keyboard, enter the value and click on the desired location.
You can create a guide parallel to an existing guide, like a duplicate: with the Construction Lines method, click on an unselected construction line in the drawing and move. Use the keyboard to enter a constrained distance.
Editing a construction line
Construction lines can be moved just like any other object: select the line, click anywhere on it and move the pointer. To constrain the translation by a definite distance, enter the desired length directly and press Return or Enter.
Absolute Origin
Click to change the origin of cartesian axes and rulers. The coordinates of the drawing and dimensions are updated automatically. You can also change the Origin by using the button on the intersection of the rulers. In HighDesign Professional each sheet has its own Origin.
Lines
Probably one of the most used tools, the Line tool allows you to trace straight lines of any length and angle from a start point to an end point.
Methods
Single Line
A line segment from one endpoint to the other.
Line by Center
Creates a line segment from its midpoint.
Segmented Line
Creates a series of connected lines. Click to set the first vertex, then click to set the next vertex. To end the series, double-click on the last vertex. Each segment is a separate line.
Double Line
Creates two parallel segments of the same length at the specified offset. Activate the Offset field next to the method icons to enter a value. Double lines can be traced from the axis or from one side.
The standard method of drawing a line of given length is to set the first point, push the L key (or the corresponding shortcut), enter the value and push the Return key. The same procedure applies to Angle (A), X, Y. More methods are described in the Basic Tasks chapter.
To resize a line, select it and with the Line tool active click one endpoint. Click its midpoint to move.
Poly-lines
The Poly-line tool creates a polygonal shape made of a connected series of straight and curved segments. Curved segments are arcs drawn by center or by tangent.
To draw a poly-line, click to set the first vertex, then click to set the next vertex. To end the chain, double-click on the last vertex.
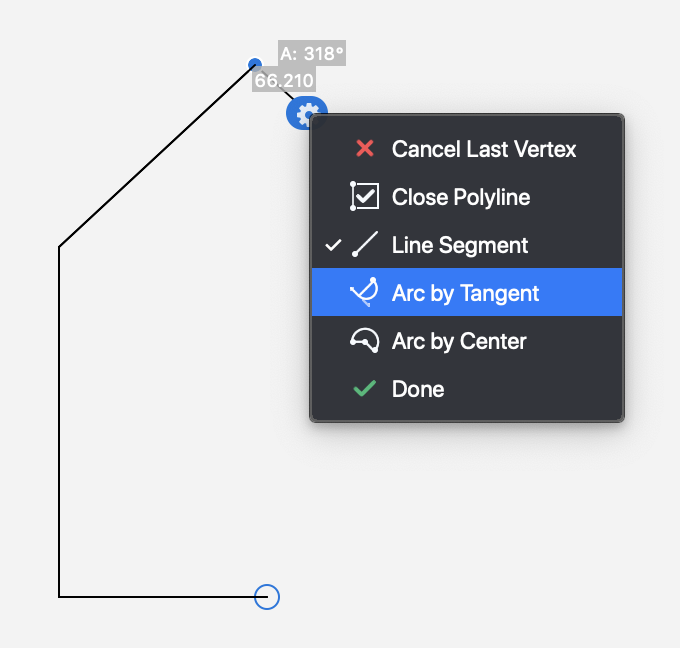
While creating a poly-line, an action icon follows the start point of each segment. Click it or hover on it to open the options menu and choose the type of the next segment, delete the last segment or end the shape. To close the poly-line, select the corresponding option or place the last vertex on the first one. Poly-lines have the fill option available in the Properties Bar.
Modifying a Poly-line
A poly-line can be edited in several ways: activate the Poly-line tool and select the object (if it’s not already selected); then:
- click a vertex to stretch it
- click a mid point to move the entire segment
- click on a segment to add a vertex
- place a vertex over another vertex to delete it
- hover the cursor on a vertex to open the Edit menu
The Object info panel provides more editing options:
- Drag the Convex slider to change the convexity of the current segment. This option can easily convert a straight segment to an arc and vice-versa. The Radius value is automatically updated when using the convexity control: you can also set the radius value numerically.
- Use the Closed switch to close the polyline. The closing segment takes the same type as the last segment added.
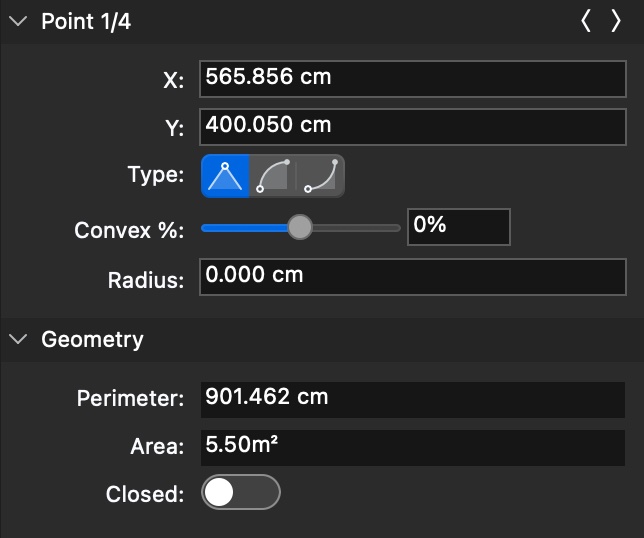
To change the type of a polyline segment from line to arc, use the Convexity controls on the Object Info panel.
Polygons
Use this tool to draw rectangles, squares and regular polygons of any number of sides.
Methods
Rectangle
To draw a rectangle, click to set the first vertex, move the pointer and click again to set opposite vertex. You can add diagonals to a rectangle by pressing the Option key on the second click. To draw a square, use the rectangle tool and hold the Shift key to constrain the diagonal direction.
To set the size of the rectangle, click to set the starting vertex, then push the “W” key to set the width and “H” to set the height. Positive values go rightwards and upwards. To edit the rectangle with either the Arrow tool or the Drawing tool active, click on vertices to resize, on midpoints of sides to stretch, and click on sides or center point to move.
Rotated Rectangle
Click to place the first vertex, move the pointer and click again to set the base angle; then move the pointer and click a third time to set the height of the shape. To set the dimensions, click the first vertex, push the “A” key to set the angle, the “W” key for the width and the “H” key for the height.
Rectangle by Center
Click to set the center of the rectangle; move and click to define the orientation and the first axis; move and click again to define the perpendicular axis.
Regular Polygon by External Radius
This method allows you to draw regular polygons with any number of sides starting from three. To set the desired number of sides, use the offset field in the Methods bar next to the tool methods and insert the value.
To draw a Regular Polygon by the external radius, click to set the center of the shape (all these regular polygons are inscribed in a circle), move the pointer and click again to set the radius of the circle circumscribed and the vertex of the polygon.
Regular Polygon by Internal Radius
This method lets you draw the polygon by setting the center and the radius of the circle inscribed in the polygon.
Regular Polygon by Side
Creates a polygon defined by the side. To create the polygon, draw the first side, exactly like a line of the desired length and angle, and click again to place the shape at the desired location.
Hatches and Fills
Use the Hatch tool to fill polygonal regions with a color, a linear vector hatch, a tiled vector pattern or a texture. This tool has four methods: Hatch region, Hatch at click, Polygonal Islands and Circular Islands.
Hatches can be chosen from a list of types: HighDesign comes with a wide range of built-in hatches that can be easily extended with your own hatches. You may also combine fills and hatches.
To set or edit hatch attributes, select Edit ▸ Settings Window ▸ Hatch Pattern or double-click the corresponding icon in the Tools bar to open the Hatches & Fill Settings window.
Hatches and Fills Settings Window
The Settings window displays all options for the graphic properties specific to the tool and the controls and fields for tool setup.
On the top bar of the dialog, close to the title, is available the triangular button to select and load existing styles: on the right there is the Add icon which allows to create a new style by the current settings. These general features of the title bar of the Settings window are shared by all drawing tools with specific settings.
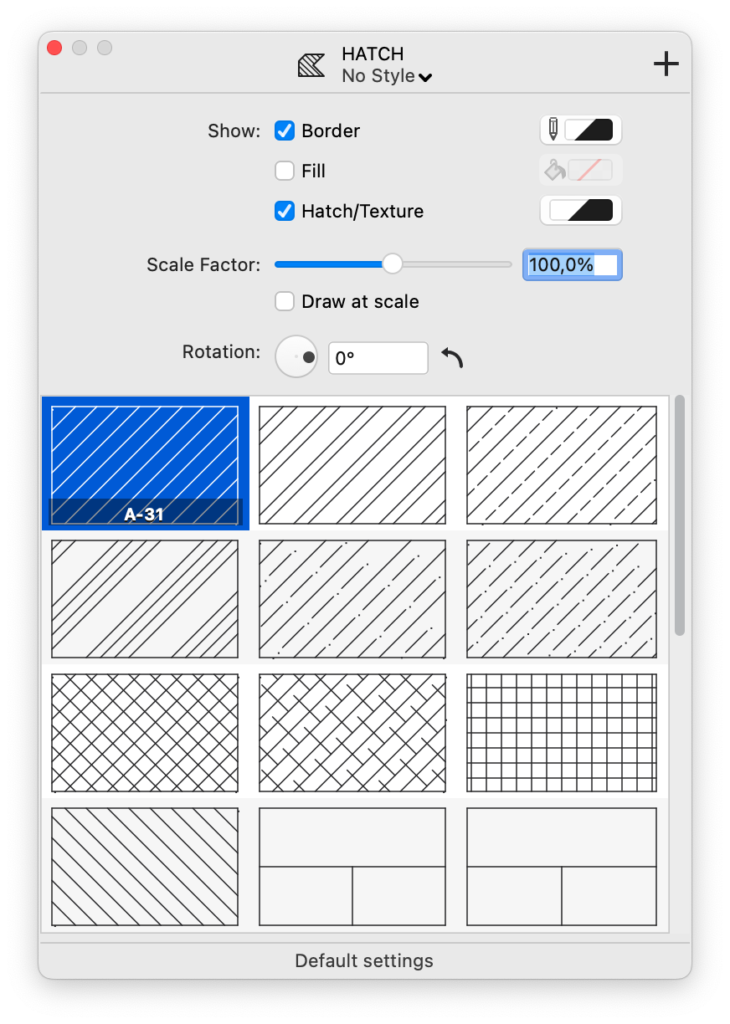
The Settings options are:
- Border: select to show the border of the hatched region and select its color.
- Fill: select to add a solid color or gradient fill. Use the fill color button to select the color and options.
- The Hatch/Texture checkbox enables the vector hatching of the region; the color of the hatch can be selected via the Pen Color menu on the Properties bar.
- Scale Factor: use this slider to scale spacings and offsets of the hatch or to resize the tile of the texture.
- Draw at scale: adjusts the scale of the hatch to match the current sheet scale, so as to resize the hatch accordingly. This option is especially useful when the hatch represents an actual construction element like a floor or a wall.
- Rotation: controls the rotation angle of all the patterns of the hatch. Textures can only rotate by 90 degrees.
- Hatches table: lists all installed hatch types, including any custom types.
- The last cell of the Hatches table is a special button: click it to add hatch types to the current project. This option opens the “Hatch patterns” pane of the Resource Manager window.
Draw and Edit a Hatch / Fill
- To draw a Hatch/ Fill region, use this tool in the same manner as the Poly-line tool or select an existing polygon and choose Tools ▸ Apply Hatch. While drawing a Hatch / Fill region, it is possible to delete the last vertex with a click on the X icon close to it.
- To edit a vertex of a hatch region, select the object and, with the Hatch tool active, move the pointer over the vertex till the tool menu shows up with the edit options.
- To add a vertex, click on one side or click on the “Add Vertex” option of the menu; to erase a vertex, move the pointer over that vertex and click on the corresponding option of the tool menu.
- The “Fit arc at click” option shows up when the pointer is over the start point of an arc and allows the user to edit the selected hatch and fit the arc with a click on it.
Hatches can also be inserted on homogeneous shapes with a click on their outline.
Hatches and Fills can host multiple openings of polygonal and circular shapes. These openings are called islands and there are two different tool methods to create them.
Methods
Hatch By Polygon
To define a polygonal hatched region, click on each vertex of the region and double click to end.
Hatch regions support only straight segments, but can be applied to arcs with a specific command available on the tool popup menu. To apply a hatch to an arc, do the following:
- Create the hatch by clicking the vertices of the outline. While defining the hatch boundary, do not follow the profile of the arc with the hatch points. Instead, add the chord of the arc between its start and end points.
- Select the hatch you just created, move the pointer over one of the points at the start or end point of the arc and hover for half a second. The options popup menu opens.
- Select Fit Arc at Click and click on the arc.
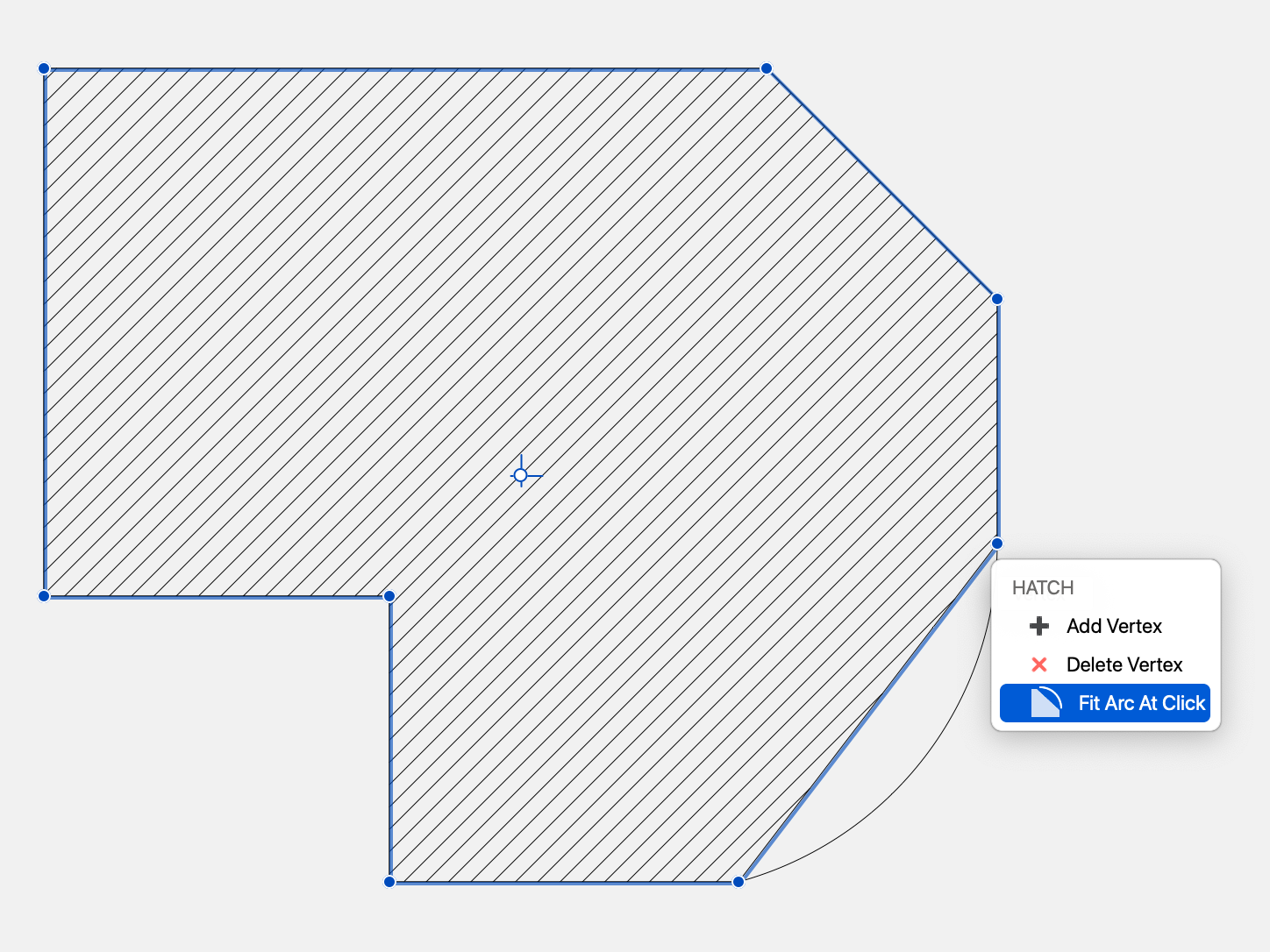
Hatch at Click
Use this method to apply the current hatch to shapes defined by lines, poly-lines, polygons, arcs, curves and other graphic objects: click inside the shape to fill it automatically with a Hatch object. The shape must be made of objects of any of the supported classes and connected at their end points.
Object classes supported by the Hatch at Click method:
- Lines
- Poly-lines
- Rectangles and regular polygons
- Arcs, Circles, Ellipses
- Bezier paths and splines
- Walls
With the exclusion of walls, the other objects can be combined together to form the base shape. For example, you can apply the hatch to a shape made of lines and arcs, or lines and a spline. Move the pointer over the shape to see the preview of the boundary of the hatch that is going to be created.

If you want to ignore the automatic boundary defined by walls and use another shape instead, hold the Alt key down. This will force the tool to ignore the region defined by the walls and look for any other region enclosing the click point.
The new hatch or fill is created with current default properties defined in the Hatch Settings panel. As with other objects, you can select it at any time and change its properties.
The hatch is automatically inserted behind the boundary shape, so that its Z position is immediately below the lowest object of the boundary. Hold the Shift key down to insert it on top of the shape.
Opening islands with the Hatch at Click method
The Hatch at Click method can be used to open islands (holes) inside a hatch: select the hatch and click on one or more shapes inside its boundary. Only the edited hatch object must be selected.
Polygonal Island
Select this method to create polygonal openings in existing hatches by drawing the shapes of the islands within the selection. To do this, just activate the Hatches & Fills tool, select the method and click on the vertices of the polygonal opening you wish to create within the hatch. This method can be used on either selected and unselected hatches. The nearest hatch is detected automatically as you move the cursor over the project.
Circular Island
This method allows you to open circular islands defined by center and radius. Click to set the center and click again to set the radius: it is also possible to set the value of the radius numerically.
To edit the island, select the hatch and locate the pointer over one vertex of the opening till the tool menu shows up giving you the options to remove the island, to delete one vertex or to add another one.
Circles, Arcs, Ellipses
Use this tool to draw circles, arcs, ellipses and arcs of ellipse. All the methods for circular arcs can be used to draw full circles by clicking the switch that appears on the screen next to the first point of the arc, or by holding down the Alt key.
The construction can be both graphical, via clicks on the drawing, or numerical via the keyboard input.
Methods
Arc/Circle by Center and Radius
To draw an arc or circle click to set the center (or set it with by coordinates), then select the arc or circle option on the on screen floating button.
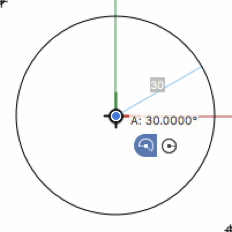
To draw an arc, set the radius by pressing the L key, set the start angle by pressing the A key and set the end angle by pressing A again. To draw an arc graphically, move the pointer and click again to set the start angle; with the next click you define the end angle of the arc.
To draw a full circle, set the length of the radius by pressing the L key on the keyboard and the start angle / end angle by pressing the A key. Press Return to confirm.
Arc/Circle by Diameter
Click to set the first vertex of the diameter, move the pointer and click again to set the second vertex. You can define the diameter by pressing the L key, and the angle by pressing the A key.
Arc/Circle by Start Point, End Point, Radius
Click to set the start point and end point of the arc and click to set the radius. The two points and the radius can also be defined via numeric input using the X, Y and Dx, Dy coordinates and L value. Hold the “alt” key to switch the direction of the arc.
Arc/Circle by Three Points
Click to set the points that define the arc. The three points can also be defined via numeric input using the X, Y coordinates or L and A values.
Arc/Circle by Tangent
Click on the endpoint of a line or on the endpoint of an arc to set the first point of the arc drawn by the tangent to that object at that datum endpoint.
Ellipse by Bounding Box
Set the start point, move and define the end point of the diagonal. The ellipse is inscribed in the rectangle defined by its diagonal.
Ellipse by Center and Radii
Click to set the center of the ellipse, move and click to define its first radius; move again and click to set its second radius. The center can also be defined by using the X, Y coordinates and the radii can be defined by pressing the L key during their construction.
Quarter of Ellipse
This method allows you to draw quarters of ellipse by clicking on its two vertices.
Curves
The Curves tool allows you to draw, single and multiple Bézier curves, Freehand lines, Spline curves and clouds.
Methods
Bézier Curves
This method can be used to draw multiple, connected Bézier paths, parametric curves defined by two vertices and two tangent lines:
- Click to set the first vertex, move the pointer and click to set the next vertex; double click to end the chain of Bezier curves.
- To draw a curve during construction, click and drag to define its profile.
The resulting path now can now be edited to smooth the vertices and turn the straight segments into the desired curves: this way the first tangent of the next curve is always defined by the previous one. Bézier curves have the Fill property: select the desired color on the “Fill color” menu of the Properties bar.
Edit a Bézier curve
- Hover the cursor over one vertex of the selected curve toshow the pop-up menu with the options to add or delete vertices and smooth or sharpen the path by creating connected curves or straight segments.
- By clicking on one of the four control points of a selected curve, you can change its position and visually adjust the profile. With multiple Bézier curves, by editing a definition point the connected tangents are constrained to keep the same angle: move the control points of the tangents to change the angle and adjust the shape of the curve.
- Hold down the Alt key while moving the control points of the tangents to edit asymmetrically; Alt key + Cmd key to disconnect the tangents.
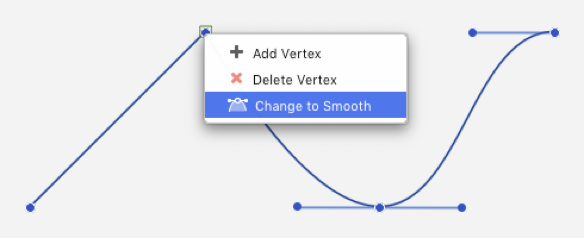
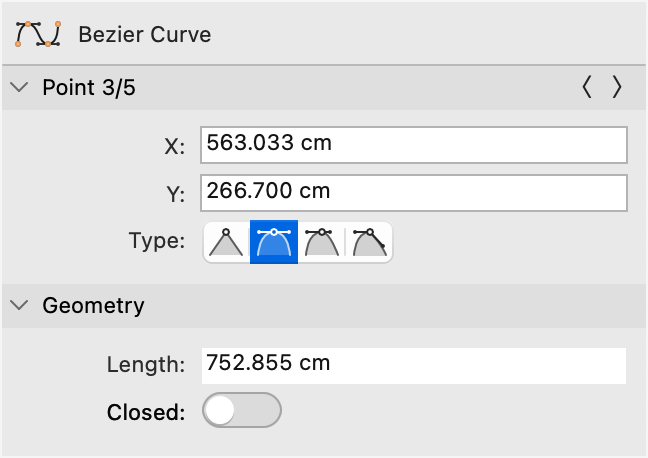
The nodes of a bézier path can also be modified through the Object Info panel: select the node and change its coordinates and node type. The node types are:
- Straight: the node has no tangents and the curve is rendered as a straight line.
- Symmetric: the tangents extend by the same length and angle on both sides of the node.
- Asymmetric: the tangents are aligned at the same angle, but different length.
- Disconnected: the tangents are totally independent and each control point has its own angle and length.
Freehand
The Freehand method lets you create spline curves by following the movement of the cursor. The freehand method has two properties: smoothing factor, that defines the complexity of the curve, and the drawing option. You can adjust the smoothing factor of new paths through the Freehand settings window: 1 means that the path will preserve its original shape, but might have many vertices; 6 is the maximum smoothing and the path will be considerably simplified.
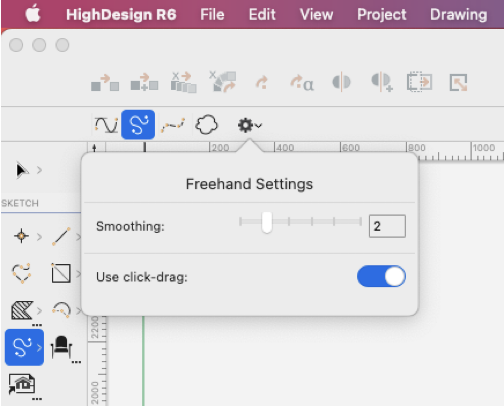
In the same pane, you can also choose to draw freehand paths with a click-drag method instead of the standard click-click: this option is specially useful when used with a pen tablet, because it allows a more natural way of drawing with a pen.
Spline
Spline curves in HighDesign are cubic B-spline, continuous curves drawn through a given set of points: to create a spline curve, click to set the points that define the shape of the curve. Double click on the last point to end the curve. Choose the fill color from the corresponding menu of the Properties bar.
Editing a Spline curve and a Freehand path
- Hover the cursor over one vertex of the selected curve to show the pop-up menu with the options to add or delete points;
- Move the given points of the selected curve with the Arrow tool or with the pointer and the Spline or Freehand tool method active.
Revision Cloud
with this method you can create a group made of chains of connected arcs. You can use this tool to draw a personal set of revision clouds to be saved as symbols for future uses.
Symbols
The Symbols Tool is a drawing tool which allows you to put in your project entire drawings or portions of drawings already created and stored in a library with just one click. Using Symbols is a convenient way for reproducing many times the same group of elements with independent rotation, mirroring and scale factors.
Symbols can store attributes, which are information displayed at the desired location of the current view.
To edit or set the Symbol Tool properties, select Edit ▸ Settings Window ▸ Symbol or double-click the Symbol Tool icon in the Drawing Tools bar.
Symbol Settings Window
The Symbol settings dialog has two panes: Symbol and Attributes. The Symbol pane provides you with many options to choose a new symbol and set its graphic properties.
- The table lists the currently selected library folder: this folder may contain many sub folders and can be organized at your choice. Browse through this table to select the symbol file.
- Once a symbol has been selected, a lists all of its views shows up if available: select a view from the list to activate it; double-click its name to change it and click on the pencil icon to edit the symbol/ view (for custom symbols only).
- The preview box displays a thumbnail of the selected symbol with the current parameters.
- Symbol geometric parameters are: width, height (which can resize proportionally), angle (in degrees); Below the input fields, the Quick transformations buttons enable the mirroring of the symbol. Symbol properties are the fill and color options and the option to scale the symbol correspondingly to the current drawing scale.
- On the bottom are grouped the buttons to (from left to right) create a new folder, create a new symbol from selected objects, duplicate the selected symbol, add a new view to an existing symbol and delete the selected item.
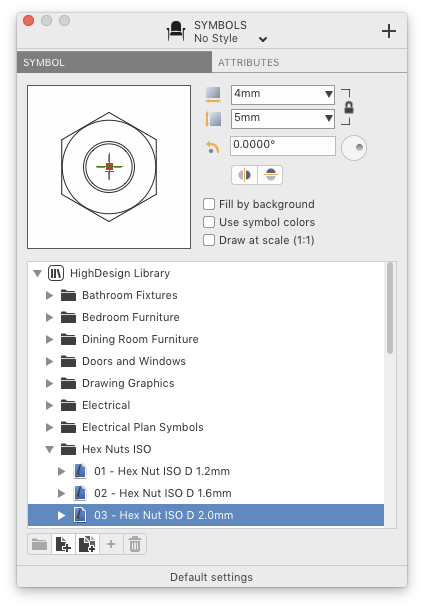
The Attributes pane displays the optional attributes of the current view. Use this pane to set the values of the attributes of the symbol or symbol view you are inserting in the project or to change the values of the current selection.
Create and Edit Symbols
The “New Symbol” and the “Edit Symbol” functions, also available through the Project menu, when activated switch to a different workspace with a limited set of tools: in this environment you can draw, modify and save symbols and symbol views.
You can either create a new symbol from scratch or create a new symbol from the selection: in this case you can also activate this function through the Radial Menu for a quicker workflow. This way the selected objects are now visible in the “Edit Symbol” environment whereas all the other elements of the drawing are hidden.
Create a new symbol:
- Select “New Symbol” on the Project menu;
- The Environment turns to the “Edit Symbol” context with a limited set of tools and the “New Symbol” dialog opens; this dialog is divided into four sections:
- Symbol Name;
- View;
- Attributes;
- Insertion Points;
- Draw the symbol;
- Type the symbol name;
- Select the destination folder through the folder button;
- Use the “+” button to add a new view;
- Type the view name;
- Set the attributes;
- Insert the attributes in the drawing of the symbol view;
- Place the Insertion Points on the desired locations of the symbol view;
- Press the “Save” button on the dialog.
Attributes of the Symbol
Attributes are information added to the current view of the symbol: these information are defined by an ID, a Prompt, showing on screen, and a Default value which will be displayed in the project.
The Attributes section of the New Symbol dialog shows:
- The menu of the existing attributes of the view (visible when editing a symbol and its attributes);
- The Add button to create a new attribute;
- The button to remove the selected attributes,
- The “Edit attribute” button to modify the currently selected attribute.
Since attributes are a sub-class of text, they can get text properties such as font, font size, alignment, style and rotation angle: the “Define Attribute” window displays all these information and options.
To insert the attribute, just click on the desired location of the symbol view.
Edit a Symbol
To edit a symbol you can click on the Edit button of the selected symbol on the Settings window, or select the symbol on the drawing and either choose “Edit Symbol” on the Project menu or use the Radial Menu.
The “Edit Symbol” workspace opens and you can modify the symbol, add views to the symbol by pushing the “+” button of the dialog or delete views through the “-” button, change the attributes of the view.
By pushing the “Save” button, the environment turns back to “Drawing”. Changes made to a symbol are immediately visible in all the symbol duplicates of the drawing.
Insert a Symbol into the drawing
- Open the Symbol Library dialog by choosing Edit ▸ Settings Window ▸ Symbol or by double- clicking the Symbol icon in the Drawing toolbar;
- Select a symbol in the Folders table and choose one of the available views;
- Set its size and optional parameters;
- Review or change the default attributes if available;
- Click one of the defined insertion points, the center or one of the vertices or midpoints of the thumbnail to select the current insertion point;
- Either drag the preview to the drawing or click on the desired point of the drawing.
To create a new symbol, to add a view to a symbol or to edit an existing symbol, are also available the specific commands on the Project menu.
Images
Images in HighDesign can be inserted via the Insert Image command, available on the File or Project ▸ Insert menus. The supported file types are TIFF, JPG, PNG, GIF and PDF. Alpha levels present in TIFF and PNG files are preserved. Once inserted into the project, the image is treated as a vector object with coordinates, width, height and angle parameters.
Insert an Image
HighDesign lets you easily add pictures to your project from several graphic formats (TIFF, JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, PDF). Images inserted into the project keep their resolution and are displayed at the real print size: it is possible to handle them as any other vector entity. PNG and TIFF images are imported with their alpha channel if present.
You can insert a picture in your project in several ways:
- File ▸ Insert Image…
- Project ▸ Insert ▸ Image…
- Double click the Image tool icon to open the Settings pane, push the Open Image button and the Open button on the pop-up panel.
- Drag and drop an image file from the computer.
- Drag and drop a picture from another application, such as a web browser or a photo archiving software.
- Paste a picture from the system clipboard.
The selected image is ready to be inserted: click anywhere on the project to insert it.
The Insert Image tool provides a popup window for the quick selection of images used in the current project or recently loaded.
PDF documents can be inserted as high-resolution images. When you choose a PDF document with the Insert Image command, you are presented with a dialog where in you can select the page to import, if more than one, and set the resolution at which the image object will be created.
Images can be moved, resized and rotated, either via the editing tools, the Object Info panel, or the Image Settings window.
Image Settings
The Image Settings window displays the following options to set size on screen, print size, resolution and transparency of images:
- Size: the dimensions of the image object in the project, measured in points, millimeters, inches or percentage;
- Image Resolution, in Dots Per Inch.
- Display at screen resolution: when active, the image is always displayed at the resolution of the screen, which is typically lower than paper. The visible size of the image is larger at lower resolutions.
- “Restore Original Values” button, to reset image size and resolution as in the source image
- Transparency: sets the amount of transparency the image is displayed at. Values range from 0%, totally opaque, to 100%, totally transparent.
- File Format: images are handled like other vector objects and saved in the project file. The internal format can either be PNG, which preserves the full quality of the image, or JPEG, which compresses the image and saves file size considerably, but reduces the quality. JPG is very good for photographic images, but not for images that contain line drawings, such as city maps or scanned drawings.
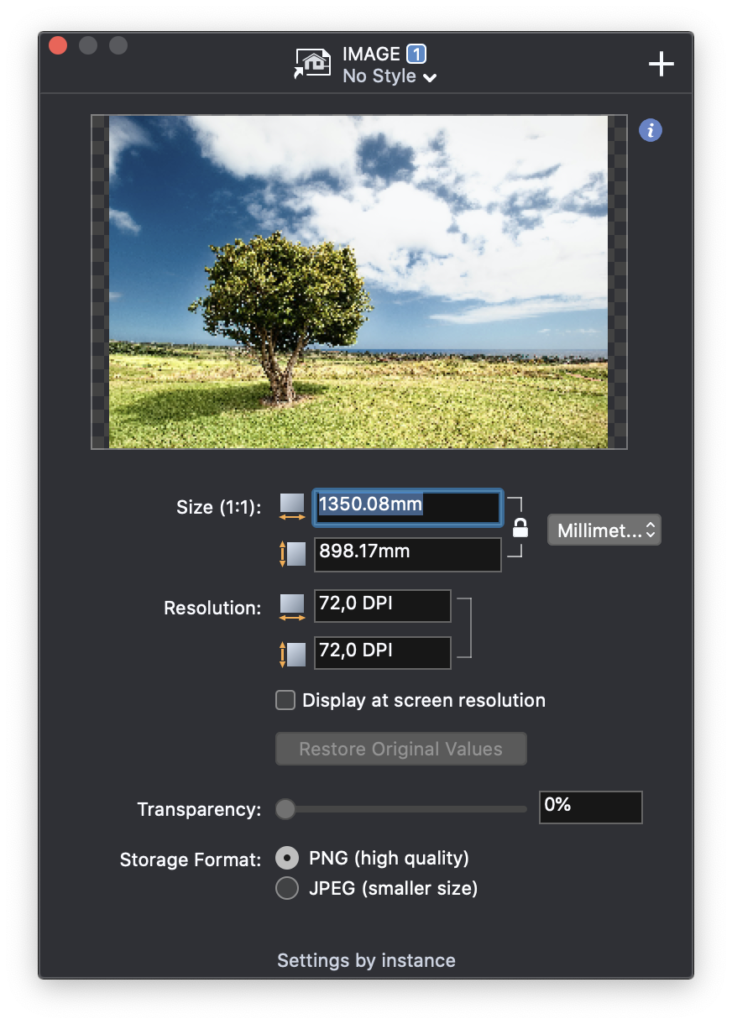
Image Size and Resolution fields allow numerical changes. Please note that the Size/Resolution ratio is constant and therefore, when changing the size, the resolution will change accordingly and vice versa.
Use the “Info” button close to the Image Preview to show the information of the source image on its preview canvas. Provided information are: file size, creation and modification dates, location of the file, image dimensions expressed in pixels and its resolution.
When the pointer hovers over the Image Preview the “Replace Image” button appears: click on it to select a new source image to insert within the existing image box.
Groups
HighDesign provides the ability of grouping different objects together as a single item. Most editing operations and transformations can only be applied to selected items, either to individual objects or to a group of objects at once.
Groups are a convenient way of organizing items by binding heterogeneous items in one “collection” which behaves as one object. Once a number of drawing objects are grouped together you can select them simply by clicking any of the group members. By default, the grouped objects retain their attributes, such as color, line type, weight, etc. Changing the attributes of a group applies the changes to all its members.
Group functions
All commands connected with groups area available in the Project menu. The functions to manage groups are Group, Ungroup, Automatic Grouping, Ungroup All, Edit Group.
- “Group” creates a new group with all the currently selected items;
- “Ungroup” breaks the selected groups;
- “Add to Group” includes selected objects in the currently selected group;
- “Automatic Grouping” is an option that automatically creates groups with items of a shape, i.e. rectangles, regular polygons, poly-lines, walls, etc.;
- “Ungroup All” breaks all groups, including those not selected.
- “Edit Group” opens a workspace where you can modify the selected group by editing, adding or removing members by using the normal drawing tools.
Edit a Group
Grouped objects can be edited all together like a single drawing object by stretching the handles of the bounding box of the group with the Arrow tool. A group can be moved, rotated, mirrored or scaled like any other object.
- A group can be resized and moved with the Arrow tool. Properties applied to a group are applied to all the group members.
- To select individual members of a group, hold down the command key and click the object. The object will be selected and available to to be modified or deleted. This method is more suitable for quick editing operations.
- You can also modify the members of a group through the Edit Group command.
The Edit Group workspace
You can activate the Edit Group workspace by selecting a group and clicking the Edit icon on the top-left handle point or by choosing Project ▸ Edit Group… This workspace opens a panel with specific commands that let you manage sub-groups, show or hide the context, add objects to the group or remove objects from it.
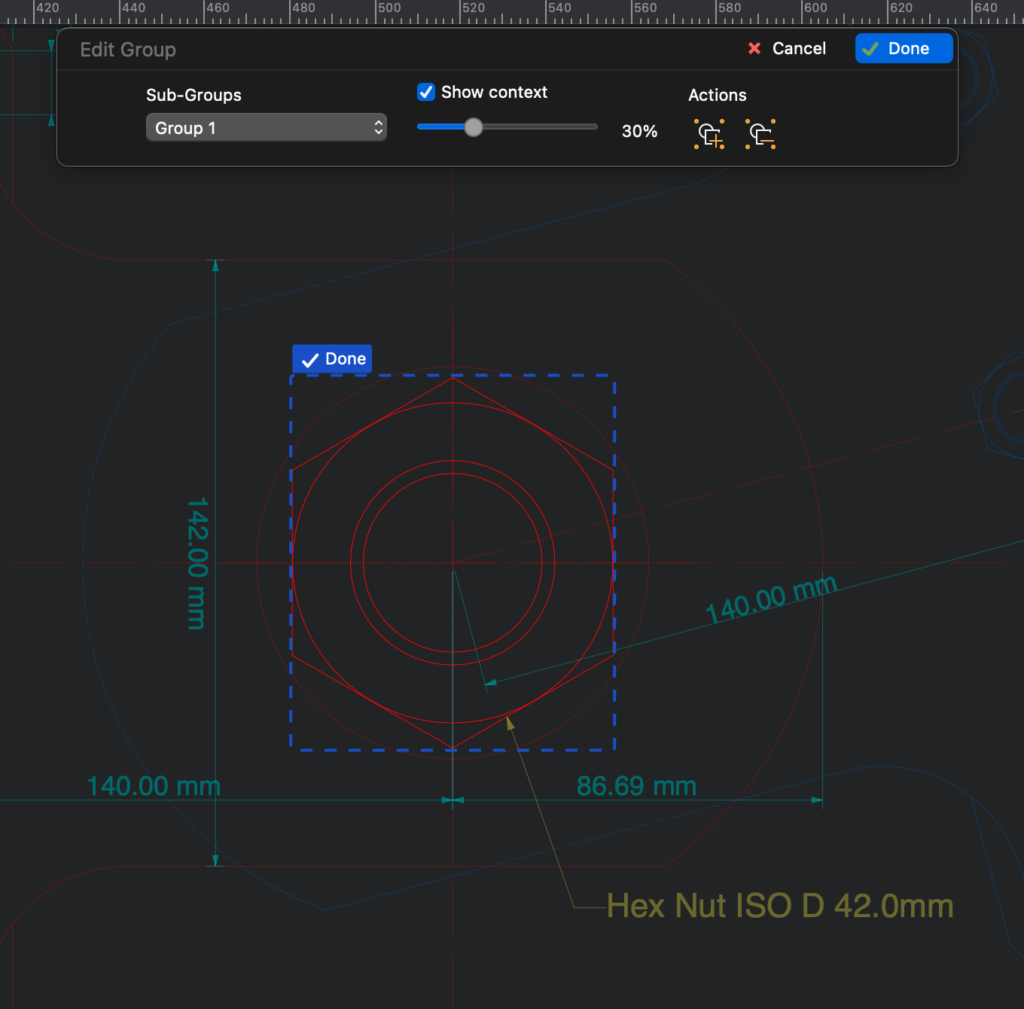
If the group includes sub-groups, you can use the Sub-Groups menu to activate any sub-group or return to the main group. To edit a sub-group, click the Edit icon above its top-left corner. Click “Done” to end the edit.
By default, the edited group is displayed within its context, that is, the surrounding objects of the drawing it is inserted into. You can adjust the level of opacity of the context or disable it altogether.
To add an existing object to the group, push the Add Object button in the Actions section and click any object in the context. In likewise manner, push the Remove Object and click on any object of the group to remove it from the group. The removed object will be moved to the sheet where its original group resides.
You can also draw any class of object using the tools that are available on the Toolbox. Any object created in this way will be added to the current group.
Push Done to confirm the changes and return to the normal workspace, or push Cancel to dismiss all the changes made in the Edit Group workspace.